Electrical functions
● Equipotential screen
● Capacitive current collection/draining
● Short-circuit draining
Protection functions
● Water barrier
● Mechanical protection
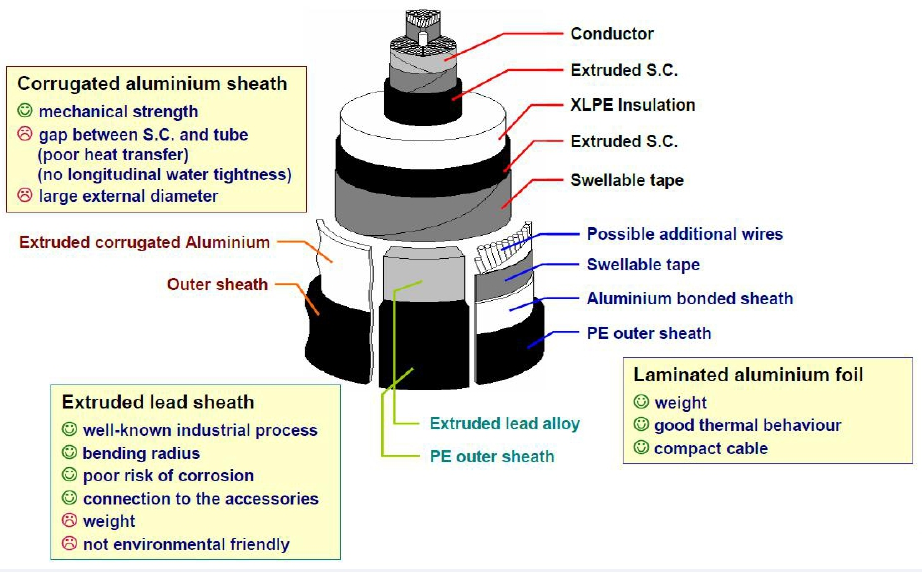
Design of the metallic screen / sheath
Main designs for HV cables
● To provide moiture barrier function
■ Extruded sheath
♦ Lead sheath
♦ Aluminium corrugated sheath
■ Longitudinally welded corrugated sheath
♦ Aluminium sheath
■ Longitudinal tape (laminated foil)
♦ Copper or aluminium
♦ Stuck with overlap or seam welded
●To provide short-circuit draining (but not
watertight)
■ Copper helically lapped tapes
■ Concentric wires
♦ Copper or Aluminium
Typical solutions
● Lead sheath
● Aluminium corrugated sheath
● Aluminium laminated foil
Possibility to combine concentric wires
● For large short-circuit currents
Main features of the typical solutions
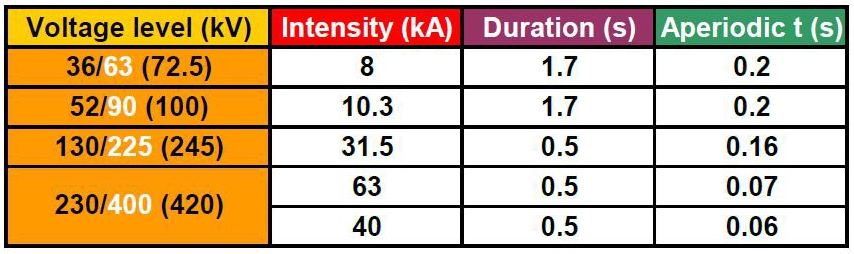
HV short-circuit data
Short-circuit test
● 3 shots
♦ 1st: conductor temperature = 90+/-4°C
♦ 2nd and 3rd = 80+/- 4°C
● Visual inspection between shots
♦ No test loop damage, especially at connections
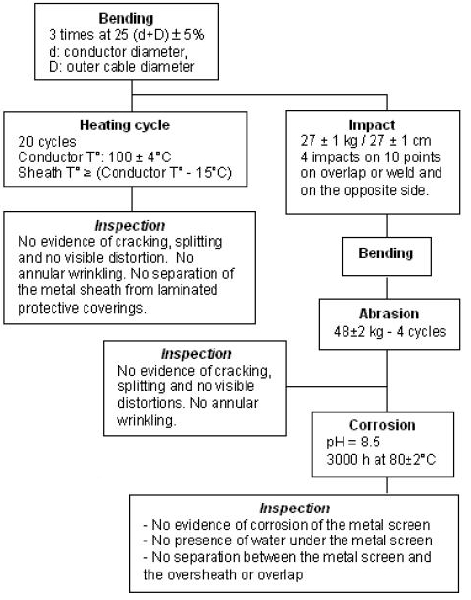
Specific tests
A primary set of tests
● to assess the watertightness of cable designs after exposure to mechanical stress
Others tests to assess
● mechanical properties only
♦ impact test and abrasion test
● radial watertightness after shrinkage
● radial watertightness after short circuits
Long term test
●200 m loop of cable with accessories
♦ 1.7 U0, 6000 hours / 250 thermal cycles






.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)





